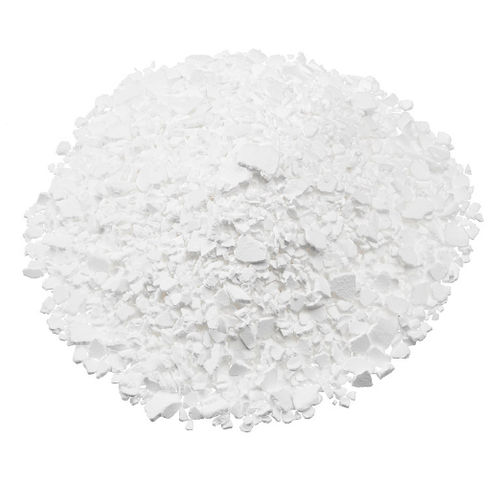
Lactose Monohydrate
Lactose Monohydrate Specification
- Storage
- Store in a cool, dry place in tightly closed container
- Molecular Weight
- 360.31 g/mol
- Structural Formula
- C12H22O11H2O
- Smell
- Odorless
- Molecular Formula
- C12H22O11 H2O
- Loss on Drying
- 5.0%
- Ph Level
- 4.5 - 7.0 (10% solution)
- Assay
- 98.0% - 102.0%
- Heavy Metal (%)
- 0.001%
- Shelf Life
- 36 months
- Moisture (%)
- 4.5% - 5.5%
- Water Solubility
- Readily soluble in water
- HS Code
- 17021100
- Taste
- Slightly sweet
- EINECS No
- 600-073-4
- Grade
- Pharma Grade / Food Grade
- Chemical Name
- Lactose Monohydrate
- CAS No
- 10039-26-6
- Usage
- Pharmaceutical excipient, food additive, used in infant formula and tablets
- Purity(%)
- 99.5% Min
- Appearance
- White crystalline powder
- Application
- Used as a diluent or filler in pharmaceutical tablets and capsules; food industry for confectionery, dairy, and bakery products
- Packaging
- 25 kg fiber drum / bag
- Melting Point
- 202C (loss of H2O)
- Particle Size
- Available as 40 mesh, 100 mesh, 200 mesh etc.
- Chloride Content
- 0.02%
- BSE/TSE Status
- BSE/TSE free
- Allergen Status
- Allergen free
- Microbial Limits
- Total aerobic microbial count: 1000 cfu/g, Yeast & molds: 100 cfu/g, E. coli & Salmonella: Negative
Lactose Monohydrate Trade Information
- FOB Port
- Mundra Port, Nhava Sheva
- Payment Terms
- Paypal, Letter of Credit (L/C), Western Union, Letter of Credit at Sight (Sight L/C), Telegraphic Transfer (T/T), Cash in Advance (CID), Cash Advance (CA)
- Supply Ability
- 100 MT Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 30 Days
- Sample Policy
- Within a certain price range free samples are available
- Packaging Details
- As Per Buyer Requirements
- Main Export Market(s)
- Australia, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Western Europe, Central America, Africa, South America, Asia, North America
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
- Certifications
- ISO, GMP, WHO, FDA, MSDS
About Lactose Monohydrate
Lactose (C12H22O11) is milk sugar. It is a disaccharide composed of one galactose and one glucose molecule. In the pharmaceutical industry, lactose is used to help form tablets because it has excellent compressibility properties. It is also used to form a diluent powder for dry-powder inhalations. Lactose may be listed as lactose hydrous, lactose anhydrous, lactose monohydrate, or lactose spray-dried.
Chemical Names:5989-81-1; Alpha-D-Lactose monohydrate; Alpha-Lactose monohydrate; Lactose monohydrate; Lactose, monohydrate; A-Lactose monohydrate
Molecular Formula: C12H24O12
Molecular Weight: 360.312 g/mol
Pharmaceutical and Food Applications
Lactose Monohydrate is highly regarded for its versatility as a diluent and filler in pharmaceutical tablets and capsules, ensuring uniform drug distribution. In the food sector, it is favored for its functional properties in confectionery, dairy, and bakery products. Its safety, purity, and consistent performance make it suitable for infant formula and other sensitive applications.
Quality, Safety, and Compliance
This product adheres to rigorous quality control standards, including limits on microbial content, heavy metals, and moisture. Being BSE/TSE-free and allergen-free, it aligns with international safety regulations. Its consistent particle size distribution and high solubility enhance both processing and end-product quality.
Packaging, Storage, and Shelf Life
Lactose Monohydrate is supplied in robust 25 kg fiber drums or bags to preserve integrity during storage and transit. The recommended storage is in a cool, dry environment within tightly closed containers, guaranteeing a shelf life of up to 36 months. Proper handling ensures the product retains its quality and performance for an extended period.
FAQs of Lactose Monohydrate:
Q: How is Lactose Monohydrate used in pharmaceutical and food industries?
A: Lactose Monohydrate serves as a diluent and filler in pharmaceutical tablets and capsules, promoting uniformity and ease of processing. In the food industry, it acts as a functional additive in products like confectionery, dairy, and baked goods, as well as an ingredient in infant formula due to its purity and safety profile.Q: What are the key benefits of using Lactose Monohydrate?
A: Key benefits include its high purity (minimum 99.5%), excellent solubility in water, neutral odor and taste, and established safety profile (BSE/TSE and allergen free). Its consistent particle size allows for reliable formulation, making it suitable for sensitive applications in both pharma and food sectors.Q: Where should Lactose Monohydrate be stored for optimal quality?
A: For best results, Lactose Monohydrate should be stored in a cool, dry location in tightly closed containers. This practice protects the ingredient from moisture and contaminants, preserving its shelf life and functional properties.Q: What is the typical packaging for Lactose Monohydrate?
A: Lactose Monohydrate is usually packaged in 25 kg fiber drums or bags, ensuring safe transport and minimizing contamination risks. This packaging supports easy handling and storage for bulk users, such as manufacturers and suppliers.Q: How does the manufacturing process ensure quality and safety?
A: The manufacturing process adheres to stringent standards for microbial counts, heavy metal content, and moisture control. Regular testing ensures compliance with international regulations, and the product is certified free from BSE/TSE and common allergens, making it fit for a wide range of applications.Q: When does Lactose Monohydrate lose water and what is its melting point?
A: Lactose Monohydrate has a melting point of 202C, at which it also loses its crystalline water. This property is crucial for understanding its behavior during processing in high-temperature applications.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Pharmaceutical Excipients Category
Aluminium Hydroxide
Molecular Formula : Al(OH)3
Storage : Room Temperature
CAS No : 21645512
Molecular Weight : 78 g/mol Ounce (oz)
Grade : Industrial / Pharmaceutical
Purity(%) : 98%
Calcium Chloride
Molecular Formula : CaCl2
Storage : Room Temperature
CAS No : 10043524
Grade : Tech Grade
Purity(%) : 94 %
Ammonium Sulphates
Molecular Formula : (NH4)2SO4
Storage : Room Temperature
Molecular Weight : 132.14 g/mol
 |
REWINE PHARMACEUTICAL
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry